LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) batteries have gained popularity as a reliable and long-lasting energy storage solution in RV or marine areas. However, charging these batteries requires careful consideration to maximize their performance and lifespan. In this blog post, we will discuss some common mistakes to avoid when charging LiFePO4 lithium batteries, ensuring that your investment in this advanced technology remains effective and efficient.
1.Avoid Using Incompatible Chargers
One common mistake when charging lithium-ion batteries is using chargers that are not designed for them. Chargers specifically designed for lead-acid batteries operate at different voltages and currents, which can cause irreversible damage to lithium-ion batteries. Using incompatible chargers can also pose safety risks such as fires, explosions, and personal injury.
To ensure safe and effective charging, always refer to the safety instructions provided by the battery manufacturer. They will recommend a compatible charger for their specific lithium-ion battery. It's essential to follow their directions and use only the original charger provided with the battery. Using a lithium battery charger for your lithium battery is not only safer but also speeds up the charging process.
Although there is a vast amount of information available online, it's important to be cautious and avoid misinformation about chargers. Just because someone claims to have used an incompatible charger successfully in the past does not guarantee the same results for your battery. If you have any doubts or questions about charging, it's best to contact the manufacturer directly. They can provide you with accurate information and, if necessary, assist you in purchasing a new charger. Taking a do-it-yourself approach can jeopardize both the longevity of your battery and your safety, so it's always better to rely on the expertise of the manufacturer.
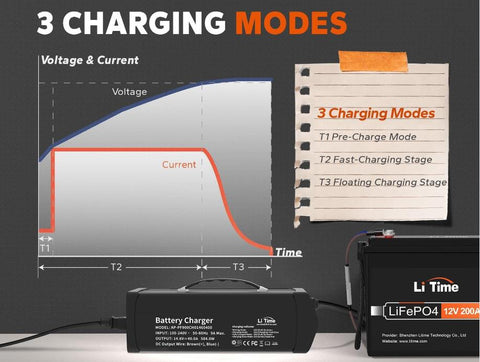
2.Avoid Using a Charger With the Wrong Voltage/Amps
It is crucial to verify the charger's voltage before connecting it to the battery to prevent any damage. During charging, make sure that the amp-hour (Ah) rating of the charger is not higher than the Ah rating of the battery. Using a charger with a higher Ah rating can cause significant harm to the battery. Being mindful of these factors will help ensure the safe and efficient charging of your lithium batteries.
If you are not sure, looking at the format below.

3.Avoid Overcharging
It is important to be aware of the possibility of overcharging lithium-ion batteries. While smartphones and laptops typically have built-in safeguards against overcharging, this may not be the case for larger lithium-ion batteries used in applications such as RVs, boats, or homes.
Overcharging a lithium-ion battery can cause lithium ions to plate onto the anode, resulting in the formation of small deposits of reactive lithium metal. This can lead to short-circuiting and potential hazards. Additionally, overcharging can cause the breakdown of the battery's electrolyte, leading to the generation of excessive heat and a thermal runaway reaction.
Fortunately, most lithium-ion batteries include safety features to prevent overcharging. However, it is still important to follow the manufacturer's instructions to ensure proper usage and avoid potential risks. Signs of an overcharged battery include swelling, leakage, excessive heat, smoking, and a decrease in performance capabilities.
4.Avoid Over Discharging
To avoid potential damage and hazards, it's important to prevent both overcharging and deep discharging of lithium-ion batteries. When a battery is discharged too much, the internal metal plates can be permanently damaged, rendering the battery useless.
To address this, most lithium-ion batteries have built-in protective features that maintain specific voltages. For example, they are designed to stop discharging once they reach a voltage of around 2.5 volts. At this point, the battery will no longer provide power to the device it is connected to. It might seem like the battery is completely drained, but it still has a small amount of remaining capacity.
When a battery reaches the low-voltage state, it can still draw power if left unattended. If the battery remains in this state for an extended period, it will eventually drop to absolute zero voltage, which means the battery is completely dead.
Fortunately, advanced lithium-ion battery systems in electric vehicles (EVs), heavy machinery, and electric boats incorporate a battery management system (BMS) to prevent overcharging and deep discharging. These systems monitor the battery's voltage and automatically cut off the load if it reaches a dangerously low level. Additionally, they have circuits in place to prevent overheating during operation or charging.
5.Avoid Charging in Extreme Environments
Although LiFePO4 batteries are less sensitive to temperature rather than lead-acid batteries, extreme heat or cold can have detrimental effects on their performance and lifespan.
Charging lithium-ion batteries in high temperatures can lead to a dangerous thermal runaway reaction. This occurs when the battery's internal heat surpasses its heat dissipation capability, resulting in a chemical reaction that can cause fires or explosions. It is crucial to charge lithium-ion batteries in a suitable environment to ensure safety and extend their longevity.
In addition to avoiding extreme heat, it is equally important to prevent the exposure of lithium-ion batteries, including LiFePO4 batteries, to extremely low temperatures. Cold temperatures can have a detrimental effect on battery performance and can even lead to permanent damage if not managed properly.
When charging batteries in low-temperature environments, the chemical reactions within the battery slow down, resulting in reduced efficiency. This can cause a decrease in charging speed and overall capacity. In extreme cases, such as below freezing temperatures, the electrolyte inside the battery can freeze, causing irreversible damage to the battery's internal structure.
To prevent these issues, it is recommended to charge lithium-ion batteries at temperatures within the specified range provided by the manufacturer. This range typically falls between 0°C and 45°C (32°F to 113°F) for most LiFePO4 batteries. Charging at temperatures outside of this range can lead to decreased performance and potentially shorten the battery's lifespan. If you live in the areas that have long winter, it’s recommended to use the battery with low temperature protection, like LiTime 12V 100Ah TM. When the temperature is below 0°C (32°F), the BMS will cut off the charging.
Can also learn more about cold weather series battery.
Additionally, exposing lithium-ion batteries to water or submerging them beyond their protective seals can trigger similar chemical reactions that result in extensive damage. While lithium-ion batteries can withstand minor exposure to moisture, it is vital to avoid submerging them to prevent any potential negative effects.
By charging lithium-ion batteries in a controlled environment and protecting them from extreme temperatures and water exposure, users can ensure the safe and optimal performance of their batteries.
6.Avoid Rapid Charging Without Balance
This suits for the battery system that batteries are connected in series or parallel.
One common mistake to avoid when charging LiFePO4 batteries is rapid charging without proper cell balancing. LiFePO4 batteries are made up of multiple cells connected in series and parallel to achieve the desired voltage and capacity. During the charging process, each cell may reach its full capacity at different times, leading to voltage imbalances among the cells. If these imbalances are not addressed, some cells may be overcharged while others are undercharged, resulting in reduced battery performance and potential damage.
To prevent cell voltage imbalances, it is crucial to use a charger that supports cell balancing or an external cell balancer. Cell balancing ensures that all cells reach their full capacity simultaneously, improving the overall performance of the battery and prolonging its lifespan. By using a charger with built-in balancing features or connecting an external balancing device, users can effectively manage and maintain cell voltage equality during the charging process.
7.Avoid Incorrect Storage before Charging
Properly storing LiFePO4 batteries before charging is crucial to maintain their performance and longevity.
When storing LiFePO4 batteries, make sure to keep them in a cool and dry environment, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. It is recommended to store LiFePO4 batteries at a partial state of charge, typically between 30% to 50%, to prevent self-discharge during storage.

LiTime 12V 100Ah LiFePO4 Batteries SOC
Before connecting a stored LiFePO4 battery to a charger, carefully inspect it for any physical damage or signs of swelling. If any issues are detected, do not proceed with charging the battery, as it may pose safety risks. Instead, contact the battery manufacturer or a professional for further assistance and guidance.
Conclusion
Properly charging LiFePO4 batteries is essential for their optimal lifespan and performance. To ensure this, it is crucial to avoid common charging mistakes such as overcharging, using incompatible chargers, disregarding the state of charge, and charging in extreme environments. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your LiFePO4 batteries provide efficient and safe power for an extended period.








