When it comes to electrical systems, one of the most important factors to consider is voltage. The voltage determines how much power can be delivered to a device and plays a crucial role in determining the overall performance of an electrical system. In this article, we will explore the differences between three commonly used voltages: 12V, 24V, and 48V. Visit LiTime RV Battery to learn more.
Table of Content
Understanding Volts and Amps and Their Importance
Volts and amps are fundamental units that measure electricity and its potential to power equipment. Volts represent the force that pushes energy through resistance, while amps measure the amount of energy that flows through a circuit.
With low volts, you may have a large amount of energy, but it requires more amps flowing through your equipment to get it moving, which can cause it to heat up and potentially lead to damage. In contrast, higher volts require fewer amps to produce the same amount of energy due to their strong force. This makes them more efficient and easier on your equipment.
It is important to note that lower volts require higher amps, which can be damaging to your equipment and increase construction costs for materials that can withstand high loads. Therefore, it is crucial to strike a balance between volts and amps to ensure optimal performance and minimize the risk of damage.
Differences Among 12V, 24V and 48V
12V System
The majority of RVs use a 12-volt system. This system is used to power the RV's lighting, water pump, vent fans, appliances, and other low-power devices. It’s generally powered by a lead-acid battery bank or deep cycle AGM batteries. Nowadays, upgrading the RV battery systems to LiFePO4 batteries is a new trend, for their higher energy, longer lifespan and more advantages. If your requirements are below 3000W, you can usually use a 12V system. Visit LTime 12V solar system kits to choose the battery for your RV.

24 System
A 24-volt system is less commonly found in RVs compared to the 12V system. In some instances, RVs may have a 24V system for specific high-powered applications such as larger motors or air conditioning units. However, it may also require specialized hardware and wiring which can make it more complex and expensive than 12V systems.
48V System
The 48-volt system is much less common and typically only used in very large RVs, buses, or custom conversions designed for off-grid living or heavy-duty workloads. It requires specialized hardware and wiring along with more expensive components which can increase the cost of setup.
The choice of voltage system depends on the specific needs of the RV owner and how they plan to use their RV. For most typical applications, a 12V system is sufficient and the most practical option. However, if the RV owner has heavy power needs or uses many high-wattage appliances, a higher voltage system may be necessary to meet those demands.
Pros and Cons of 12V System
Pros
- Simplicity: Many people understand 12V systems, making it easier to find help with your system. Most RVs are designed to work with 12V house battery banks.
- Commonality: 12V systems are more common than any other voltage, which means replacement parts will be easier to find at better prices. Alternator Charging: Most alternators and chassis batteries are 12V, making charging through a battery combiner easier.
- DC Distribution: Most DC loads run on 12V, so powering them directly is possible.
- Battery Expansion: With a 12V lithium battery bank, you can add to your system with one battery at a time.
- Solar Expansion: A higher voltage solar array requires more series-connected cells or panels, which makes the solar array less resilient to partial shade.
- Heated Batteries: Some heated lithium batteries only work in parallel configuration (12V systems), which is necessary for cold climates.
Cons
- Thicker Cables: Lower voltage means higher current, requiring thicker cables, which can add cost and complexity to your system.
- Inverter Limitation: The largest inverter you would want to power with a 12V system will be 3000VA, limiting your options if you need more capacity.
Pros and Cons of 24V System
Pros
- Higher Wattage: Lower voltage means higher current, requiring thicker cables, which can aWith a higher battery voltage compared to a 12V system, there is less current, which allows for more wattage on 4/0 cable. 24V systems are ideal when you need to run two air conditioners at the same time on a 5000VA inverter.
- Larger Solar Array: A 24V battery bank allows you to double the solar array capacity without purchasing an additional solar charge controller.
- Increased Efficiency: When running heavy loads like DC air conditioners, there will be a slight efficiency increase on a 24V system compared to a 12V system.
- Increased Maximum Battery Bank Size: With a 24V battery bank, you can have eight batteries since you would be using four parallel groups of two in a series connection.
Cons
- DC Distribution: A 24V to 12V converter will need to be used to power DC loads.
- Battery Expansion: In most cases, adding to a lithium battery bank will require adding two batteries at a time.
Pros and Cons of 48V System
Pros
- High Output: Due to the higher voltage and lower current, 48V systems can have high output inverters like 8000VA and larger.
- Largest Battery Capacity: With fewer parallel battery connections, 48V systems can have the largest battery banks.
Cons
- RV Compatibility: RVs require elaborate alternator charging and DC distribution systems when using 48V house batteries.
- Technical Know-how: Few technicians know how to work with 48V, making it more suitable for Electrical Engineers who like to tinker.
How to Choose 12V VS 24V 48V
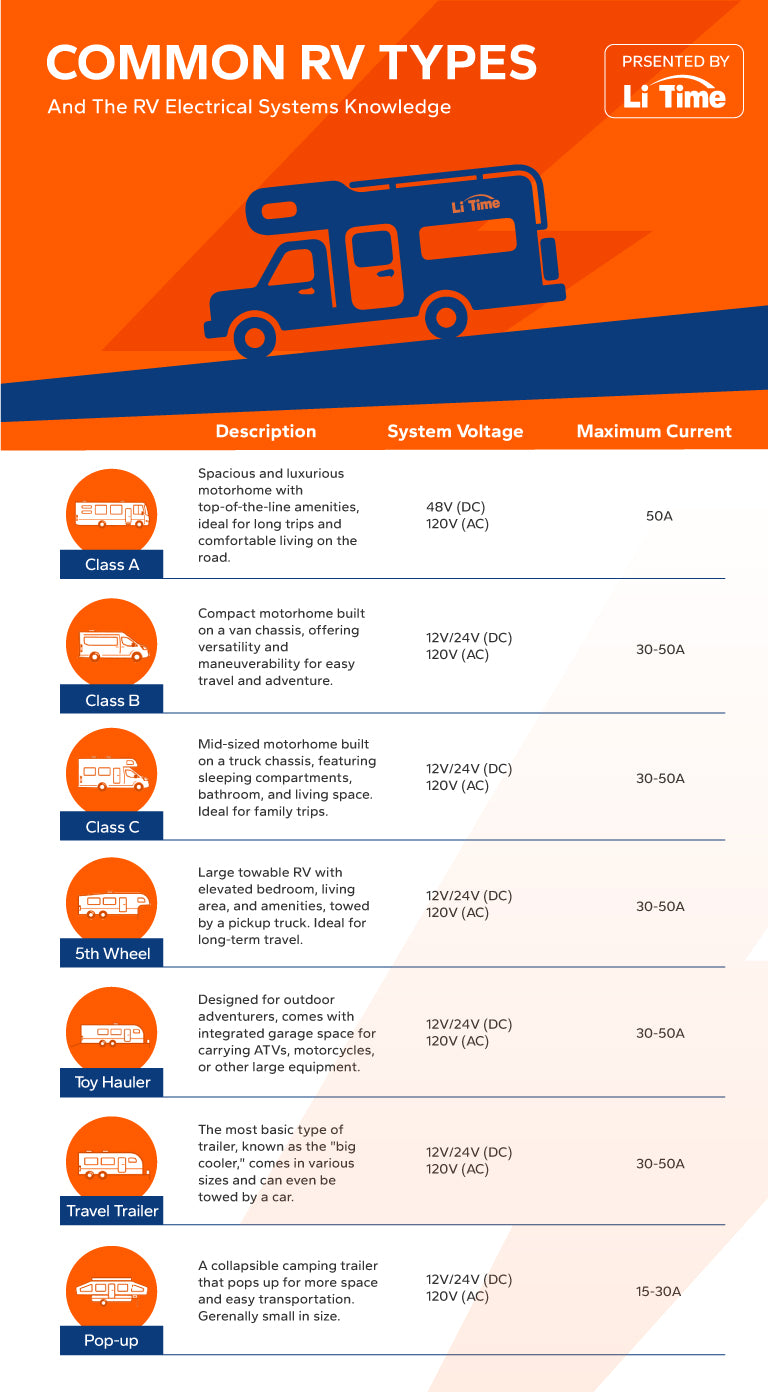
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question because you need to determine your specific situation in order to make the choice. Regarding the electrical system in an RV, if your RV is relatively small, such as a B-class, Toy Hauler, Pop-up, etc., and there is limited space for appliances and electrical usage, a 12V system may be more suitable. However, for larger RVs like A-class, 5th Wheel, etc., a higher voltage system, such as 24V, or 48V, may be more appropriate because there is more space for appliances and wiring and the cost of wiring is high which can be effectively reduced.
If you find you need more energy than 12V, try to connect the batteries in series and parallel to get more power.

Typical Appliances and How Much Current They Draw
|
Appliances used in an RV EQUIPMENT |
Max CURRENT |
|
RV Air Conditioner (Start-up) |
12-15 Amps |
|
RV Air Conditioner (Running) |
3-6 AMps |
|
Chargers (small electronics) |
0.5 to 1.5 Amps |
|
Coffee Pot (Brewing) |
7-9 Amps |
|
Coffee Pot (Warming) |
1-3 Amps |
|
Crock Pot (Cooking - High) |
3-5 Amps |
|
Crock Pot (Warming) |
1-2 Amps |
|
Food Processor |
5-8 Amps |
|
Frying Pan (Cooking - High) |
7-10 Amps |
|
Hair Dryer (High) |
7-12 Amps |
|
Heater, Electric (Small Space) |
4-10 Amps |
|
Iron (High) |
8-10 Amps |
|
Microwave Oven (Standard) |
7-9 AMps |
|
Microwave Oven (Convection) |
7-14 Amps |
|
PC, Notebook |
1-3 Amps |
|
Refrigerator (2-door medium size) |
2-4 Amps |
|
Toaster |
8-10 Amps |
|
TV, Digital |
1-3 Amps |
|
Vacuum (Hand-Held) |
2-4 Amps |
|
Water Heater (6-gallon, heating) |
8-12 Amps |
Looking for a reliable solar energy solution for your RV? Look no further than LiTime. Our comprehensive one-stop shop includes top-quality products such as LiFePO4 batteries, chargers, solar panels and more.
Our products are designed to provide you with the best value for your money, and we're committed to offering dependable solutions that you can count on. Whether you're looking to upgrade your existing RV system or install a new one, LiTime has got you covered.
If you have any questions about our products or services, don't hesitate to get in touch with us at service@litime.com. We're always happy to lend a helping hand and provide you with the support you need to make informed decisions about your energy needs.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Learn more about
<<< Step By Step- How to Hook Up Solar Panels to RV Batteries








