In today's fast-paced world, the demand for quick and efficient charging solutions for lithium batteries has significantly increased. With the emergence of fast charging technologies, consumers are often left wondering about the trade-offs between slow and fast charging methods.
This article aims to provide comprehensive insights into the charging speed of lithium batteries, comparing the benefits and drawbacks of slow charging versus fast charging.
Is Fast Charging Best for Lithium Batteries?
Lithium batteries come in different types, the most common being lithium-iron phosphate batteries and ternary lithium batteries. Generally, the former is suitable for slow charging, while the latter is designed for fast charging. The suitability for fast charging is primarily reliant on the battery type and the manufacturer's design of the battery performance.
The performance of lithium battery charging is determined by the internal settings of the charger, which cannot be altered by users. Manufacturers configure the ports of slow charging versus fast charging based on the specific characteristics of the battery, and the Battery Management System (BMS) uniformly manages the charging process. It is crucial to adhere to the manufacturer's requirements during the charging process to ensure safety.
At present, LiTime lithium batteries capable of accommodating 1C charging include the 12V 100Ah Max, 36V 55Ah lithium trolling motor battery, and the batteries utilized in golf carts. For other batteries, we still advocate using 0.2C for charging.
LiTime 12V 100Ah Max Lithium Deep Cycle Battery
Charging lithium batteries using original chargers does not typically support fast charging. Utilizing a fast charging station of the pulse type may lead to damage to the battery's protective plate, increasing the likelihood of malfunctions. A broken protection board within a lithium battery can result in significant issues. Unlike lead-acid batteries, lithium batteries require a two-stage charging process involving constant voltage and constant current.

The charge and discharge rate of a lithium battery is determined by the charge and discharge current within the unit's rated capacity, usually denoted as "C." While faster charging at higher currents reduces the charging time, it also intensifies battery heating. Over time, the maximum charging current a lithium battery can accept diminishes due to the polarization phenomenon, potentially leading to issues such as reaction decomposition of electrolyte and gas production, impacting the safety and lifespan of the battery.
What Are the Risks of Fast-Charging Lithium Batteries?
The installation requirements and costs of lithium battery charging equipment are high due to the need to handle high current and voltage, exerting significant stress on the battery over a short period.
Prolonged rapid charging can impact the lifespan of the lithium battery. Fast charging inputs a large current into the battery instantaneously and repetitive use of this mode diminishes the battery's ability to recover, reducing the total number of charge and discharge cycles.
Moreover, fast charging places substantial demands on the quality of lithium batteries, leading to considerable damage to battery life and a notable reduction in safety, hence its use should be minimized when not essential.
The principle of lithium battery fast charging involves an initial voltage increase followed by a surge in current. This high current accelerates the reaction within the battery, generating excessive heat due to internal resistance, surpassing safe temperature limits, ultimately causing damage or premature aging of the battery.
Slow Charging VS Fast Charging
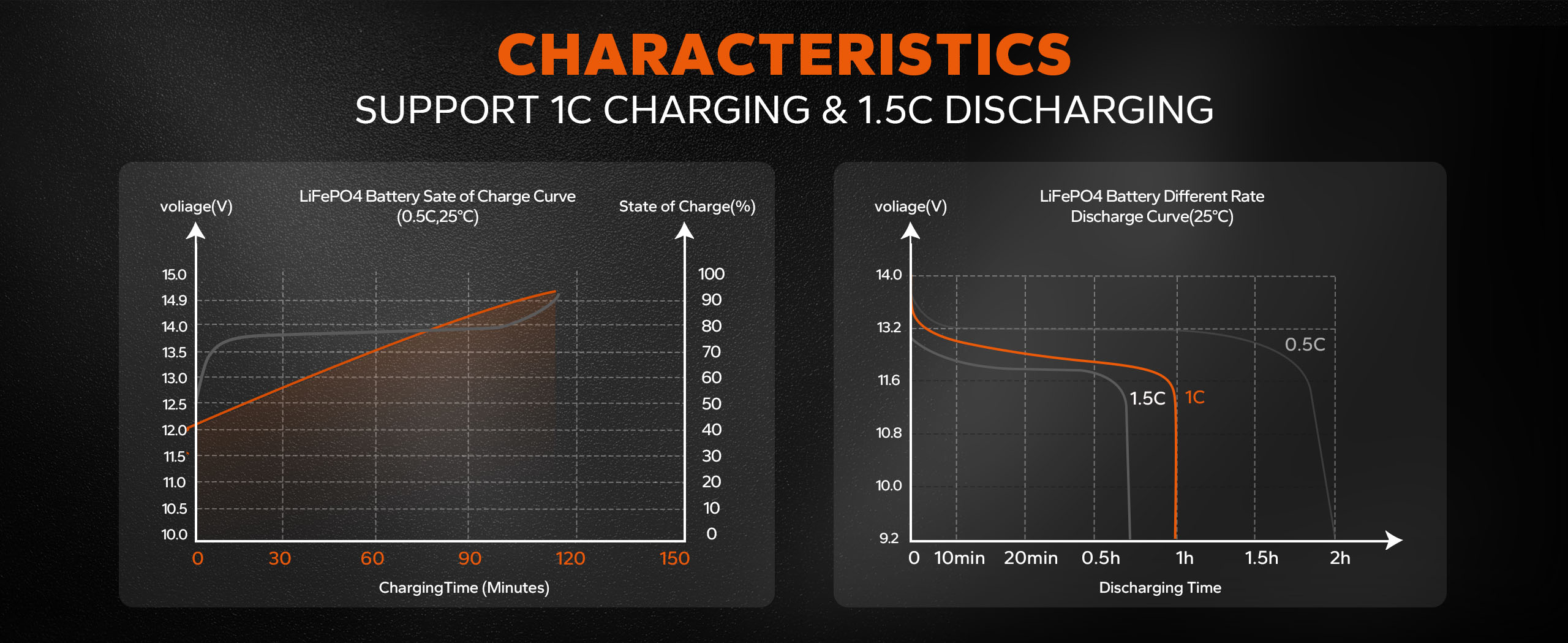
Regarding slow charging vs fast charging of lithium batteries, fast charging typically involves high-power DC charging, capable of reaching 80% battery capacity within half an hour, while slow charging entails AC charging, extending the process to 6 to 8 hours.
The swiftness of fast charging stems from variations in charging voltage and current. Higher current results in faster charging. Upon nearing full capacity, the charging mode transitions to a constant voltage, preventing overcharging and safeguarding the battery.
Slow charging employs relatively low charging current and power, promoting battery longevity and offering cost-effective charging during low power consumption. Conversely, fast charging demands higher current and power, significantly impacting the battery pack and its lifespan. Fast charging also necessitates additional supporting equipment such as AC to DC converters, elevating overall costs.
However, it's important to note that continuous reliance on fast charging can substantially abbreviate the lifespan of lithium batteries. When using slow charging, the battery's cycle life typically extends to over 3,000 cycles, whereas consistent fast charging can reduce the cycle life to approximately a thousand cycles, or even fewer. Therefore, understanding the implications and trade-offs between slow charging and fast charging is vital for battery longevity.
Manufacturers of electric vehicle lithium batteries have analyzed that sudden increases in risk factors, especially related to the production of gas and the decomposition of electrolytes, can significantly affect the safety and lifespan of lithium batteries.
In conclusion, while lithium battery chargers can be crafted according to charging requirements, whether lithium batteries can be fast charged depends on the manufacturer's specifications. It is important to understand the charging capabilities of specific lithium batteries to avoid potential issues related to fast charging.
FAQs about Charging Lithium Batteries
1. What are the most recommended ways to charge lithium batteries?
There are 3 reliable ways to charge:
- Using lithium battery charger
- Solar Panels with solar charge controller
- Generator/Alternator with DC-DC charger
Read on Best Ways to Charge LiFePO4 Battery to learn more details.
2. How long does it take to charge?
It depends on the state of charge (SOC) of the lithium battery. It is optimal to maintain lithium battery power levels within the range of approximately 20-85%.
Charging periods that are excessively brief or prolonged can diminish battery lifespan, and in extreme cases, may even lead to safety incidents. The commonly referenced "8 hours of charging" indicates that when the battery is entirely depleted, some batteries necessitate approximately 8 hours for full recharging.
3.When is the best time to charge lithium battery
The best time to charge a lithium battery is when it reaches around 20-30% capacity remaining. This level offers the most efficient and effective charging process while also avoiding the potential for over-discharge, which can negatively impact the battery's overall health and lifespan.
Related reading: How Do You Store LiFePO4 Lithium Battery
Conclusion
In the realm of lithium battery charging, the choice between slow charging and fast charging ultimately comes down to striking a balance between battery longevity and charging speed. While slow charging offers benefits in terms of battery health and safety, fast charging provides unparalleled convenience and time efficiency.
As fast charging technologies continue to evolve, it is essential for both manufacturers and consumers to consider the long-term implications of charging speed on the overall performance and lifespan of lithium batteries.








