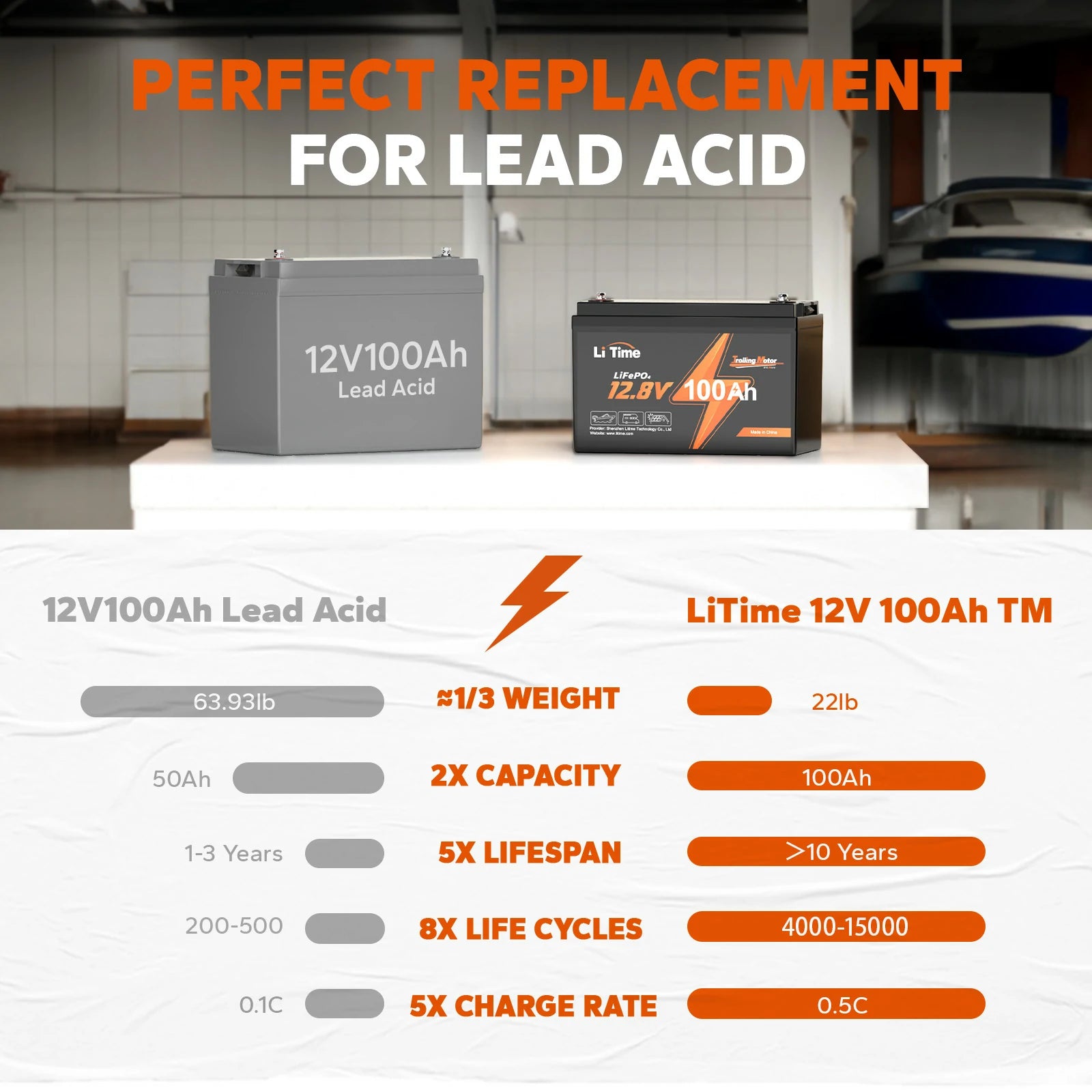
Lithium batteries have become an indispensable part of our modern lives, powering a wide range of devices from smartphones to electric vehicles. However, one concern that often arises is whether lithium batteries are prone to leakage.
In this article, we will explore the topic of lithium battery leaks, understand the causes and effects, and discuss preventive measures to ensure safe usage.
Understanding Lithium Batteries
Lithium batteries are rechargeable power sources that utilize lithium ions to store and release energy. They typically consist of a positively charged cathode, a negatively charged anode, and an electrolyte solution. These batteries offer numerous advantages such as high energy density, longer lifespan, and low self-discharge rates compared to traditional battery types.
Do Lithium Batteries Leak?
Yes, lithium batteries have the potential to leak. Normally, lithium batteries do not leak electrolytes or other chemicals under normal conditions. However, under abnormal conditions, leakage may occur. Several factors can contribute to the leakage of a lithium-ion battery. Poor manufacturing quality and improper use can increase the likelihood of a lithium battery leaking. Additionally, short circuits pose the greatest risk to lithium batteries.
Factors Contributing to Lithium Battery Leaks
Lithium-ion batteries generally have low instances of leakage, but there are specific scenarios in which leakage can occur. Here are some examples of contributing factors:
1. Physical Damage
Physical damage to the battery, such as punctures or dents, can compromise the integrity of the battery casing and lead to leaks.
Reputable lithium battery manufacturers take precautions to minimize the risk of leakage, often performing drop testing on their products. This testing assesses the batteries' durability and ability to withstand damage. By choosing a reliable brand like LiTime, you can increase the likelihood of obtaining a battery less prone to leaks.
2. Manufacturing Defects:
Poor manufacturing quality, including flaws in the sealing process or improper assembly of the battery components, can create weak points where leaks can occur. Therefore, trustworthy manufacture is important when choosing the lithium battery. The LiFePO4 lithium batteries from LiTime have past the test of UL, FCC, CE, RoHS, UN38.3.
3. Overcharging:
Overcharging a lithium battery can cause it to release excess heat and pressure, potentially leading to leaks if the battery's safety mechanisms fail to prevent it.
4. High Temperatures:
Exposing lithium batteries to high temperatures or extended heat can lead to degradation and a higher risk of leaks. If a lithium battery exceeds its recommended temperature range, it can cause the electrolyte inside to be damaged and potentially leak out. This emphasizes the importance of storing lithium batteries in a cool and dry environment. By following the manufacturer's instructions for storage, you can help minimize the chances of battery leakage.
5. Age and Wear:
Over time, lithium batteries can deteriorate and the materials inside can become less stable. This can increase the chances of leaks occurring, especially if the battery is old or has been heavily used.
6. Incorrect Storage:
Storing lithium batteries in improper conditions, such as exposing them to moisture or extreme temperatures, can accelerate the degradation of the battery and make leaks more likely.
Types of Lithium Batteries Prone to Leakage
Various types of lithium batteries exist, and it's crucial to handle them with care to prevent leaks.
The dominant lithium-ion batteries are widely prevalent in items such as cell phones, laptops, and electric cars. While they offer significant power, they are susceptible to cracking and leaking if subjected to impacts or mishandling.
Lithium-polymer batteries, which employ a different electrolyte, are commonly found in healthcare devices and electronic cigarettes. Similar to lithium-ion batteries, they can leak if damaged or broken due to their fragile nature.
A newer advancement in lithium battery technology involves the use of lithium iron phosphate. These batteries are less prone to leakage since they utilize iron instead of cobalt in their construction. However, their power output and lifespan are typically lower compared to other rechargeable battery options.
The latest innovation in lithium batteries is the lithium-sulfur type. These batteries are more environmentally friendly as they incorporate sulfur instead of lithium in their production. They also pose a reduced risk of leakage compared to other lithium battery variants.
Risks and Dangers Associated with Lithium Battery Leaks
When a lithium battery leaks, it can potentially pose several risks and dangers. It's important to be aware of these hazards and take appropriate precautions. Here are some risks and dangers associated with lithium battery leaks:
Damage to electronic devices
The leaked electrolyte from a lithium battery can corrode and damage electronic devices. This can result in malfunctions or permanent damage to the device.
Fire hazard
If the leaked electrolyte comes into contact with flammable materials, it can ignite and cause a fire. Lithium batteries contain highly flammable components, and a leak can increase the risk of a fire outbreak.
Chemical burns
The electrolyte in lithium batteries is often corrosive and can cause chemical burns if it comes into contact with your skin or eyes. It's crucial to avoid direct contact with leaked electrolyte and take appropriate safety measures.
To minimize these risks and dangers, it's important to handle lithium batteries with care, purchase quality batteries from reputable sources, and follow proper charging and usage guidelines. In the event of a battery leak, prioritize your safety by wearing protective gear and following appropriate cleanup and disposal procedures.
How to Check Weather a Lithium Battery is Leaking?
To check if a lithium battery is leaking, follow these steps:
Visual inspection
Carefully examine the battery for any visible signs of leakage. Look for wet spots, discoloration, or a build-up of residue on the battery casing.
Odor detection
Smell the area around the battery. A leaking lithium battery may emit a distinct chemical odor. If you detect an unusual or pungent smell, it could be an indication of a leak.
Check the contacts
Inspect the battery contacts or terminals for any signs of corrosion or unusual substances. Leakage may result in the formation of corrosive material around the battery connections.
Device malfunction
If the device powered by the lithium battery is not functioning properly or is behaving erratically, it could be a sign of a leaking battery affecting its performance.
Battery performance
Monitor the battery's performance. If you notice a significant decrease in battery life or if the battery drains quickly, it could be due to a leak affecting its capacity.
It's important to note that lithium battery leaks are not common under normal conditions. However, if you suspect that your lithium battery is leaking based on the above indicators, it's crucial to take appropriate safety precautions and handle the battery with care.
If confirmed, follow the previously discussed guidelines on how to treat a leaking lithium battery, or consider seeking professional assistance if you're unsure about handling it yourself. Remember to prioritize safety throughout the process.
Immediate Actions for Dealing with Leaking Lithium Batteries
Discovering a leak in your battery can be concerning, but there are a few steps you can take to address the situation immediately. Here's a method for treating lithium battery leaks:
Inspect the battery case
Check if the battery case is intact. Common causes of shell damage include improper installation, welding slag in the battery box, or impacts from the chassis. Assessing the condition of the case helps identify potential sources of the leak.
Examine the safety valve
Remove the cover plate and inspect the safety valve for any signs of acid leaks. Ensure that the valve is open and check for the flow of electrolyte into the battery. This step helps determine if there's a leakage through the safety valve.
Test the seal
If the first two steps appear normal, it's important to assess the seal's integrity. Pressurize and inflate the battery in water, looking for air bubbles. The presence of bubbles indicates a faulty seal, while their absence suggests that the seal is intact.
Remove electrolyte during charging
While charging the battery, check for the presence of electrolyte. If you notice any, carefully remove it to prevent further leakage.
Once you identify the source of the leak, cautiously clear the area using a knife. Then, apply a strong, battery-specific adhesive to seal the leaking port securely.
To reduce the likelihood of battery leaks, it's advisable for consumers to be vigilant when purchasing batteries. Look out for authentic, high-quality batteries from reputable sources.
By promptly addressing battery leaks and ensuring proper battery quality, you can mitigate potential risks and instill a safer battery usage experience.
First-Aid Measures
In the event of contact with a leaking lithium battery, follow these first-aid measures:
Contact with skin: Immediately remove any potentially contaminated clothing and rinse the affected area under running water for at least 15 minutes. Seek medical attention to ensure proper evaluation and treatment.
Contact with eyes: Flush the eyes with running water or saline solution for several minutes. Seek immediate medical attention for a thorough examination.
Inhalation: Move to fresh air as quickly as possible to avoid further exposure. Ensure a clear airway and provide oxygen if the person is experiencing breathing difficulties. If the person stops breathing, administer CPR and seek medical assistance immediately.
Ingestion: If the electrolyte is accidentally swallowed, rinse the mouth with water and follow it with milk or egg white if available. Do not induce vomiting. Seek immediate medical attention for proper evaluation and care.
These first-aid measures are general guidelines. It's essential to contact medical professionals promptly to ensure adequate assessment and appropriate treatment for any exposure to leaking lithium batteries.
Preventing Lithium Battery Leaks
Preventing lithium battery leaks is crucial for safety and optimal battery performance. Here are some measures you can take to minimize the risk of leaks:
Purchase from reputable sources:
Buy lithium batteries from reputable manufacturers and suppliers to ensure their quality and adherence to safety standards. Counterfeit or substandard batteries may have manufacturing defects that increase the risk of leakage.
Use devices with built-in safety features:
Opt for devices that have built-in protection circuits or safety mechanisms specifically designed for lithium batteries. These features help prevent overcharging, overheating, and excessive discharge, reducing the likelihood of leaks.
All of LiTime LiFePO4 lithium batteries are built-in BMS (battery management system) to protect the safety of battery using.
Regularly inspect batteries:
Perform visual inspections of your lithium batteries to check for any signs of damage or deformation. If you notice bulges, leaks, or cracks in the battery casing, it may indicate a potential leak hazard, and the battery should be replaced immediately.
Monitor battery performance:
Pay attention to any unusual behavior or decreased performance of your devices that could indicate a battery issue. Sudden drops in battery life, inconsistent charging, or unexpected device shutdowns may be warning signs of a potential leak or battery malfunction.
Handle with care:
When handling lithium batteries, avoid dropping or subjecting them to excessive force. Rough handling can damage the battery's internal structure and increase the risk of leaks.
Proper storage and transportation:
Store lithium batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight, extreme temperatures, and moisture. Use the original packaging or a battery case designed for safe storage. If transporting batteries, ensure they are securely packaged and protected to prevent physical damage.
Follow manufacturer guidelines:
Read and follow the manufacturer's instructions and guidelines for charging, discharging, and maintaining lithium batteries. Overcharging, using incompatible chargers, or neglecting recommended voltage limits can lead to leaks and other safety hazards.
Proper disposal:
When it's time to dispose of lithium batteries, follow local regulations and guidelines for safe disposal. Improper disposal can harm the environment and potentially cause leaks if the batteries are damaged or punctured during disposal.
While these precautions can help minimize the risk of lithium battery leaks, it's essential to stay vigilant and prioritize safety. If you suspect a leak or encounter any issues with a lithium battery, it's best to seek professional assistance or consult the manufacturer for guidance.
What Type of Lithium Battery is the Most Unlikely to Leak
Among the various types of lithium batteries, the lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) battery is considered one of the least likely to leak. Here's why:
Chemistry: LiFePO4 batteries use lithium iron phosphate as the cathode material, which is more stable and less prone to chemical reactions compared to other cathode materials, such as lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) used in lithium-ion batteries. The stability of the cathode material reduces the risk of electrolyte leakage.
Electrolyte composition: LiFePO4 batteries typically use non-flammable electrolytes that are more stable and less likely to leak under normal operating conditions. The choice of safer electrolytes contributes to the overall stability of the battery and reduces the risk of leakage.
Structural design: LiFePO4 batteries are often manufactured with robust casing and self-sealing mechanisms that help contain any potential leaks. The design focuses on preventing exposure to air and moisture, which can trigger unwanted chemical reactions and electrolyte leakage.
Structural design: LiFePO4 batteries are often manufactured with robust casing and self-sealing mechanisms that help contain any potential leaks. The design focuses on preventing exposure to air and moisture, which can trigger unwanted chemical reactions and electrolyte leakage.
While LiFePO4 batteries have a lower likelihood of leaking, it is still important to handle them with care and ensure proper usage and storage conditions. Following recommended guidelines and adopting good battery management practices can further reduce the risk of leaks and other safety concerns associated with lithium batteries.
LiTime: Innovating Secure, Eco-Friendly Lithium Solutions
LiTime is a renowned frontrunner in the lithium industry, renowned for its cutting-edge lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) battery systems that are both high-quality and cost-effective. Through groundbreaking cell engineering, our batteries can endure more than 4,000 deep-cycle charges, offering a remarkable service life of over 10 years under regular usage.
Here’s a drill test of LiTime 12V 100Ah Mini LiFePO4 pouch cell.
We can see even it’s drilled, there’s only some gas but no fire. Learn more reviews about LiTime.
Related Reading: Pouch VS Prismatic LiFePO4 Cells
Conclusion
While lithium batteries are generally designed to be leak-resistant, there are certain factors that can lead to leaks. Poor manufacturing quality, improper usage, and the risk of short circuits are key contributors. By understanding these factors and following proper safety measures, users can reduce the likelihood of lithium battery leaks and ensure the safe operation of their devices. Remember, responsible handling, purchasing from reliable sources, and implementing safety mechanisms are crucial in preventing lithium battery leaks and maintaining overall battery safety.